Yantai
Yantai, formerly known as Zhifu or Chefoo, is a prefecture-level city on the Bohai Strait in northeastern Shandong Province, China. Lying on the southern coast of the Korea Bay, Yantai borders Qingdao on the southwest and Weihai on the east. It is the largest fishing seaport in Shandong. Its population was 6,968,202 during the 2010 census, of whom 2,227,733 lived in the built-up area made up of the 4 urban districts of Zhifu, Muping, Fushan, and Laishan.
Contents
1 Names
2 History
3 Geography
3.1 Climate
4 Administration
5 Economy
5.1 Power
5.2 Industrial Zones
5.3 Average Height
6 Education
7 Transport
8 Tourism
9 Twin cities of Yantai
10 Notable people
11 See also
12 Notes
13 References
14 External links
Names
The name Yantai (lit. "Smoke Tower") derives from the watchtowers constructed on Mount Qi in 1398 under the reign of the Hongwu Emperor of the Ming dynasty. The towers were used to light signal fires and send smoke signals, called langyan from their supposed use of wolf dung for fuel. At the time, the area was troubled by the "Dwarf Pirates" (Wokou), initially raiders from the warring states in Japan but later principally disaffected Chinese. It was also formerly romanized as Yen-tai.[1]
The major district of Yantai is Zhifu, which used to be the largest independent city in the area. It was variously romanized as Chefoo,[2]Che-foo,[1] Chi-fu,[3] and Chih-fou. Although this name was used for the city by foreigners prior to the Communist victory in the Chinese Civil War, the locals referred to the settlement as Yantai throughout.[1][3]
History

Moon Bay in Yantai
During the Xia and Shang dynasties, the region was inhabited by indigenous peoples vaguely known to the Chinese as the "Eastern Barbarians" (Dongyi). Under the Zhou, they were colonized and sinicized as the state of Lai. Lai was annexed by Qi in 567 BC. Under the First Emperor (Shi Huangdi), the area was administered as the Qi Commandery. Under the Han, this was renamed as the Donglai Commandery (東萊郡). Following the Three Kingdoms Period, the area was organized by the Jin as the Donglai Kingdom or Principality, later returning to prefecture status as a jùn and then zhōu. Under the Tang and during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, it was known as Deng Prefecture and organized with the Henan Circuit. It was then organized as the Laizhou (萊州府) and then, under the Qing, Dengzhou Commandery (登州府).
Up to the 19th century, however, the Zhifu area consisted of nothing but small unwalled fishing villages of little importance.[1] Under the Ming, these were first troubled by the "Dwarf Pirates" and then by the overreacting "Sea Ban", which required coastal Chinese to give up trading and most fishing and relocate inland upon pain of death.
Following the Second Opium War, the Qing Empire was obliged to open more treaty ports by the unequal 1858 Treaty of Tianjin, including Tengchow (now Penglai). Its port being found inadequate, Zhifu—about 30 miles (48 km) away—was selected to act as the seat of the area's foreign commerce.[1] The mooring was at considerable distance from shore, necessitating more time and expense in loading and unloading, but the harbor was deep and expansive and business grew rapidly.[1] The harbor opened in May 1861, with its status as an international port affirmed on 22 August. The official decree was accompanied by the construction of the Donghai Pass (東海關).[4] It quickly became the residence of a circuit intendant ("taotai"), customs house, and a considerable foreign settlement located between the old native town and the harbor.[1]Britain and sixteen other nations established consulates in the town.[4] The town was initially expanded with well-laid streets and well-built stone houses, even for the poorer classes, a Catholic and a Protestant church were erected, and a large hotel did business with foreigners who employed the town as a summer resort.[1]

Original German Post Office in Yantai's old town
The principal traders were the British and Americans, followed by the Germans and Thais.[a] In the 1870s, the principal imports were woolen and cotton goods, iron, and opium and the principal exports were tofu, soybean oil, peas, coarse vermicelli, vegetables, and dried fruit from Zhifu itself, raw silk and straw braid from Laizhou, and walnuts from Qingzhou. The town also traded Chinese liquors and sundries for the edible seaweed grown in the shallows of the Russian settlements around Port Arthur (now Dalian's Lüshunkou District).[1] In 1875, the murder of the British diplomat Augustus Margary in Tengchong, Yunnan, led to a diplomatic crisis that was resolved in Zhifu by Thomas Wade and Li Hongzhang the next year.[5] The resultant Chefoo Convention gave British subjects extraterritoriality throughout China and exempted the foreign merchants' enclaves from the likin tax on internal commerce. Its healthy situation and good anchorage made it a favorite coaling station for foreign fleets, giving it some importance in the conflicts over Korea, Port Arthur, and Weihaiwei.[5]
Along with much of the rest of Shandong, Yantai was under German influence for about 20 years.[6] In the run-up to the First World War, its trade continued to grow[b] but was limited by the poor roads of the area's hinterland and the necessity of using pack animals for portage.[5] The trade items remained largely the same as before.[5] After the Germans were defeated by Allied forces in World War I, Qingdao and Yantai were handed over to the Japanese, who turned Yantai into a summer station for their Asian fleet. They also set up a trading establishment in the town.[7] The different foreign influences that shaped this city are explored at the Yantai Museum, which used to be a guild hall. However, the city's colourful history has not left a distinctive architectural mark, there has never been a foreign concession, and though there are a few grand 19th-century European buildings, most of the town is of much more recent origin.[8] After 1949, the town's name was changed from Chefoo to Yantai, and it was opened to the world as an ice-free trade port in 1984.[9]
On 12 November 1911, the eastern division of Tongmeng Hui declared itself a part of the revolutionary movement. The next day, it established the Shandong Military Government (山東軍政府) and, the day after that, renamed itself the Yantai Division of the Shandong Military Government (山東煙台軍政分府). In 1914, Jiaodong Circuit (膠東道) was established with Yantai as the capital. Jiaodong Circuit was renamed Donghai Circuit (東海道) in 1925. On 19 January 1938, Yantai participated as part of an anti-Japanese revolutionary committee.
After the creation of the People's Republic of China, Yantai was officially awarded city status with the outlying towns of Laiyang and Wendeng tacked on as "Special Regions" (专区) in 1950. Wendeng was merged into Laiyang six years later, and this larger Laiyang Special Region was combined with Yantai City to become Yantai Prefecture (烟台地区). Yantai is of strategic importance to China's defense, as it and Dalian, directly across the Bohai Sea from it, are primary coastal guard points for Beijing. In November 1983, the prefecture became a prefecture-level city.[10]
Geography
Yantai is located along the north coast of the Shandong Peninsula, south of the junction of Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea and parallel to the southern coast of Liaoning. The topographical breakdown consists of:
- 36.62% mountainous
- 39.7% hilly
- 50.23% plain
- 2.90% basin
About 2,643.60 km2 (1,020.70 sq mi) is urbanized. Only Qixia City is located entirely inland. All other county-level entities are coastal, with Changdao consisting entirely of islands. The total coastline of the prefecture is 909 kilometers (565 mi).
The summits in the hill country vary from 100–300 meters (330–980 ft); the average peak in the mountainous region is 500 meters (1,600 ft), and the highest point of elevation is the summit of Mount Kunyu (昆崳山) at 922.8 meters (3,028 ft).
There are 121 rivers over 5 kilometers (3.1 mi) in length, the largest being:
- Wulong River (五龙河)
- Dagu River (大沽河)
- Dagujia River (大沽夹河)
- Wang River (王河)
- Jie River (界河)
- Huangshui River (黄水河)
- Xin'an River (辛安河)
The core of the old town of Zhifu was located above the mouth of the Yi (沂河, Yí Hé).[1]
Climate
| Climate data for Yantai (1971–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.6 (58.3) | 19.8 (67.6) | 25.0 (77) | 31.9 (89.4) | 35.3 (95.5) | 38.0 (100.4) | 36.9 (98.4) | 36.2 (97.2) | 32.4 (90.3) | 30.4 (86.7) | 25.1 (77.2) | 18.8 (65.8) | 38 (100.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.2 (29.8) | −0.3 (31.5) | 4.8 (40.6) | 12.0 (53.6) | 17.8 (64) | 22.0 (71.6) | 24.8 (76.6) | 24.8 (76.6) | 21.1 (70) | 15.7 (60.3) | 8.4 (47.1) | 1.8 (35.2) | 12.6 (54.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −12.8 (9) | −12.6 (9.3) | −8.1 (17.4) | −2.6 (27.3) | 6.6 (43.9) | 11.5 (52.7) | 14.7 (58.5) | 15.0 (59) | 10.7 (51.3) | 0.8 (33.4) | −4.9 (23.2) | −10.8 (12.6) | −12.8 (9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 11.5 (0.453) | 9.7 (0.382) | 16.5 (0.65) | 35.7 (1.406) | 49.9 (1.965) | 70.0 (2.756) | 150.0 (5.906) | 161.6 (6.362) | 83.7 (3.295) | 39.0 (1.535) | 25.1 (0.988) | 19.8 (0.78) | 672.5 (26.478) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.4 | 5.0 | 4.7 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 8.5 | 11.7 | 10.3 | 7.1 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 7.5 | 86.0 |
| Source: Weather China[11] | |||||||||||||
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Yantai administers 12 county-level divisions, including four districts, seven county-level cities, one county, and one development zone. (开发区)
- Zhifu District
- Fushan District
- Muping District
- Laishan District
Laiyang City
Laizhou City
Penglai City- Zhaoyuan City
Qixia City
Haiyang City- Changdao County
- Yantai Economic and Technological Development Zone
- Yantai Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone
These are further divided into 148 township-level divisions, including 94 towns, six townships, and 48 subdistricts.
| Map |
|---|
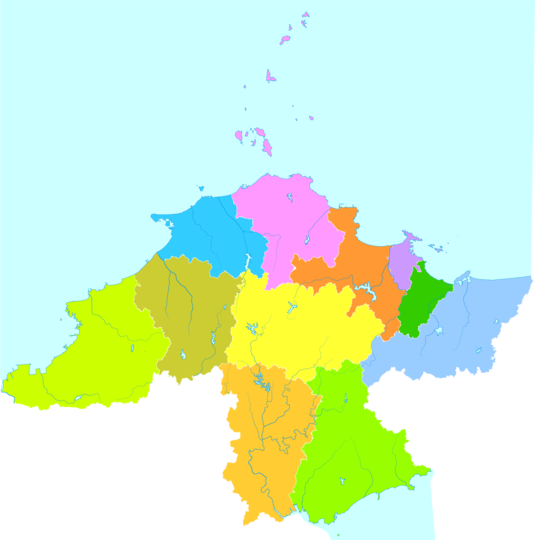 Zhifu Fushan Muping Laishan Changdao County Longkou (city) Laiyang (city) Laizhou (city) Penglai (city) Zhaoyuan (city) Qixia (city) Haiyang (city) |
Economy
Yantai is currently the second largest industrial city in Shandong, next to Qingdao. However, the region's largest industry is agriculture. It is famous throughout China for a particular variety of apple and Laiyang pear, and is home to the country's largest and oldest grape winery, Changyu.[12]

Modern day Chateau Changyu, Yantai, Shandong
The county-level city of Longkou is well known throughout China for its production of cellophane noodles.[citation needed]
Power
Yantai derives most of its energy from a large coal power plant using bituminous coal, and fitted with coal gasification technology to minimize pollution.[13] The plant is located close to Yantai port.[14]
Industrial Zones
- Yantai Economic and Technological Development Area
Yantai Economic and Technological Development Area is one of the earliest approved state-level economic development zones in China. It now has a planned area of 10 km2 (3.9 sq mi) and a population of 115,000. It lies on the tip of the Shandong Peninsula facing the Yellow Sea. It adjoins downtown Yantai, merely 6 kilometers away from Yantai Port, 6 kilometers away from Yantai Railway Station (not to be confused with Yantai South Railway Station), and a 30-minute drive to Yantai International Airport.[15]
- Yantai Export Processing Zone
Yantai Export Processing Zone (YTEPZ) is one of the first 15 export processing zones approved by the State Council. The total construction area of YTEPZ is 4.17 km2 (1.61 sq mi), in which the initial zone covers 3 km2 (1.2 sq mi). After developing for several years, YTEPZ is completely constructed. At present, the infrastructure has been completed, with standard workshops of 120,000 m2 (1,300,000 sq ft) and bonded warehouses of 40,000 m2 (430,000 sq ft). Up to now, owing to an excellent investment environment, YTEPZ has attracted investors from foreign countries and regions such as Japan, Korea, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Sweden, the United States, Canada, etc., as well as domestic investors, to operate in the zone.[16]
Average Height
The people of Yantai are known to be one of the tallest in China. As the economy prospered, height increased. The average height for 16-18 year old male students in 2010 was 176.4 cm (5 ft 9.4 in).[17]
Education
The following is a list of prominent Yantai higher education institutions.
- Yantai University
- Ludong University
- Shandong Institute of Business and Technology
It houses a Korean international school, Korean School in Yantai.
Chefoo School previously educated foreign children.
Transport
Yantai Penglai International Airport provides scheduled flights to major airports in China as well as Seoul, Osaka, and Hong Kong.[18]
Tourism

Yantai Ship Mast

Temple of the Sea Goddess
Penglai City's Dan Cliffs (丹崖) is said to be the departure point of the Eight Immortals on their trip to the Conference of the Magical Peach.[citation needed] It is important to note that Penglai is around 80Km from the city centre of Yantai.
Twin cities of Yantai
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in China[citation needed]
| Country | City |
|---|---|
| United States | San Diego |
| Japan | Beppu |
| New Zealand | Tauranga |
| Japan | Miyako |
| Russia | Vladivostok |
| South Korea | Gunsan |
| Thailand | Phuket |
| United Kingdom | Angus |
| South Korea | Wonju |
| South Korea | Ulsan |
| Sweden | Örebro |
| Bulgaria | Burgas |
| France | Quimper |
| France | Angers |
| South Korea | Incheon |
| Hungary | Szombathely |
| South Korea | Ansan |
| United States | Omaha |
| Australia | Mackay Isaac Whitsunday |
| Spain | Alcala De Henares |
Notable people
Chou Wen-chung (b. 1923), composer
Qiu Chuji (1148–1227), leading Quanzhen Taoist priest and founder of Dragon Gate Taoism
Qi Jiguang (1528–1588), Ming Dynasty military general most remembered for defending coastal China against Japanese pirates
Peter Stursberg (1913-2014), Canadian writer and journalist
Fan Bingbing (b. 1981), actress
Guanqun Yu (b. 1982), Opera singer
See also
- Chefoo School
Notes
^ In 1872, 233 British vessels entered the port with 97,239 tons of cargo valued at £144,887 and 348 ships of all other nationalities entered with 149,197 tons of cargo valued at £177,168.[1]
^ Total imports and exports were valued at £2,724,000 in 1880, £4,228,000 in 1899, and £4,909,908 in 1904. The 905 vessels in 1895 had a total tonnage of 835,248; the 1842 in 1905 held 1,492,514 tons.[5]
^ abcdefghijk EB (1878).
^ Postal Map Romanization.
^ ab EB (1911), p. 132.
^ ab "烟台概览:烟台名称源于烟台山", 腾讯新闻, 19 June 2008.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}. (in Chinese)
^ abcde EB (1911), p. 133.
^ Zhou, Yingjie (24 July 2006), "开放,三次保全了近代烟台(下)", Sina Finance. (in Chinese)
^ Jin, Long (24 July 2006). "东炮台现日军侵占烟台罪证 大理石上留印记(图)". Retrieved 19 November 2012.
^ Wang, Xin (24 July 2006). "郭显德:把西方文化传播到烟台". Retrieved 19 November 2012.
^ Liu, Xinguo (24 July 2006). "中国首批沿海开放城市之一—烟台(图)". Retrieved 19 November 2012.
^ "优越的地理环境及人文历史造成就旅游圣地烟台". 24 July 2006. Retrieved 19 November 2012.
^ [1]
^ Will Lyons (5 April 2013). "Indulge in China's Latest Export". Wall Street Journal.
^ "A report- China's coal future and public permissions for building power plants". http://www.mep.gov.cn/home/rdq/hjyxpj/jsxmhjyxpj/xmslqk/201605/W020160522142498799849.pdf. Shandong university and Shandong provincial government. Retrieved 17 July 2018. External link in|website=(help)
^ Fairley, Peter (1 January 2007). China's coal future. USA: MIT Technology review. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
^ RightSite.asia | Yantai Economic and Technological Development Area
^ RightSite.asia | Yantai Export Processing Zone
^ "Yantai average height". 2015.
^ Yantai Chaoshui International Airport project
References
 Baynes, T.S., ed. (1878), "Che-foo", Encyclopædia Britannica, 5 (9th ed.), New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, p. 455.
Baynes, T.S., ed. (1878), "Che-foo", Encyclopædia Britannica, 5 (9th ed.), New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, p. 455.
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911), "Chi-fu", Encyclopædia Britannica, 6 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press, pp. 132–3.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911), "Chi-fu", Encyclopædia Britannica, 6 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press, pp. 132–3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yantai. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Yantai. |
Government website of Yantai (available in Chinese, English, German, French, Japanese and Korean)- Old photos of Yantai (Chefoo)
- 1912 historical map of Yantai